# Docker Host VM for MariaDB
# Install CentOS 7
Download and mount the latest CentOS 7 Minimal ISO (opens new window) to the VM.
Start the VM and wait for the installer to show up.
It is recommended to stick to english as german translation is often incomplete and you get a weird mix of german and english.
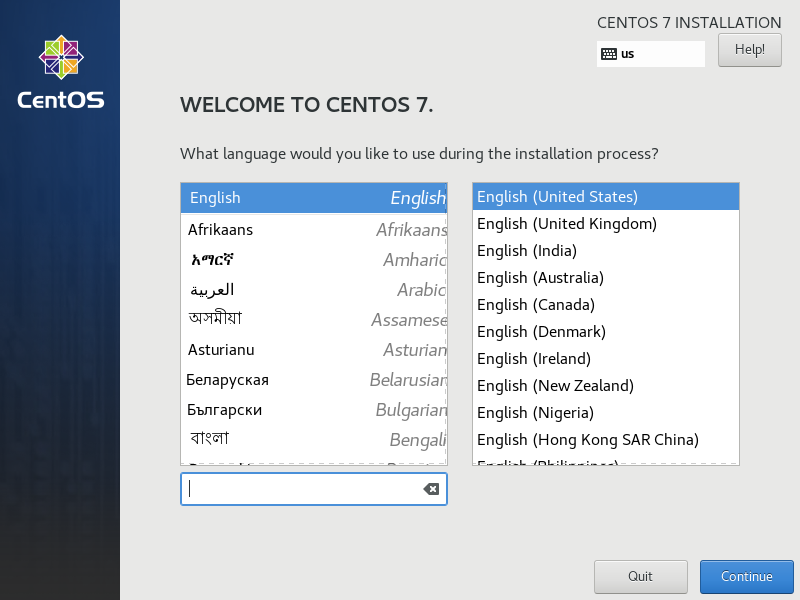
Setup Date & Timezone

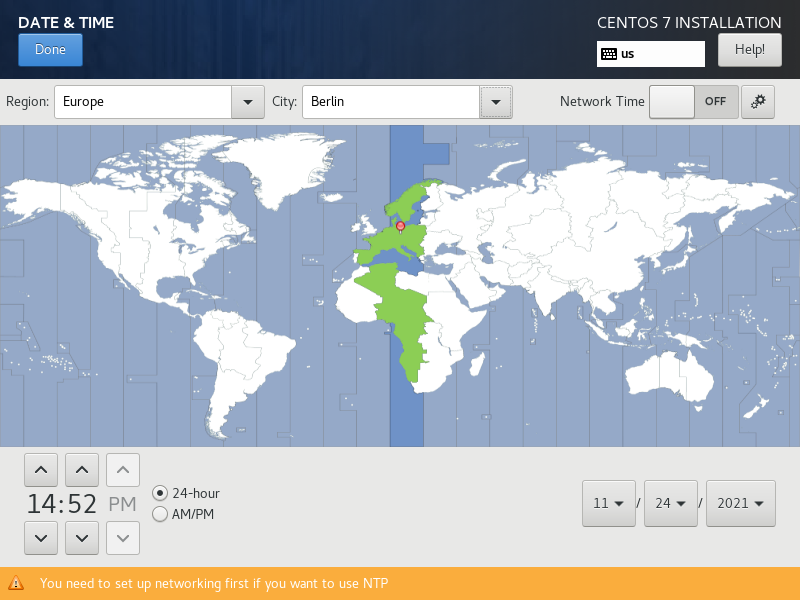
Setup a partition layout using LVM. (LVM lets us add storage later on).

Choose I will configure partitioning.
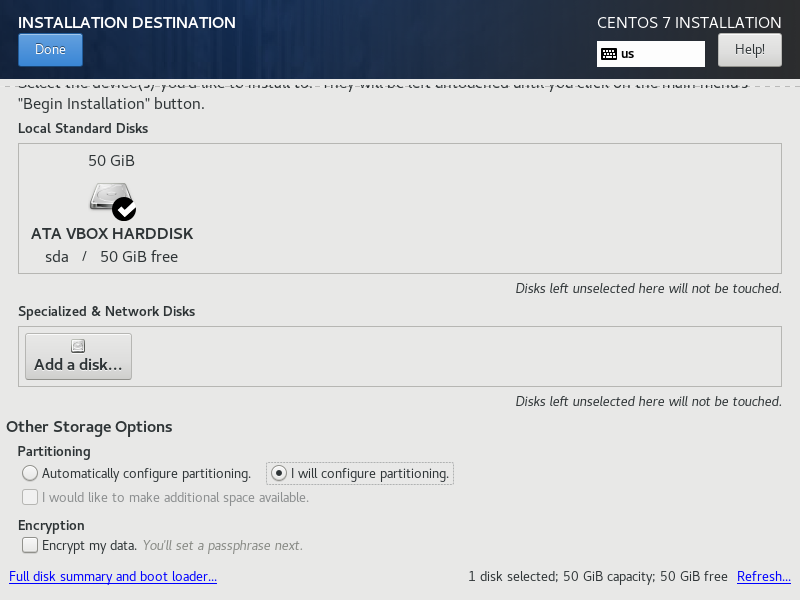
Click on Click gere to create them automatically.

Change the size of the partition mounted to / to something like 15GB.
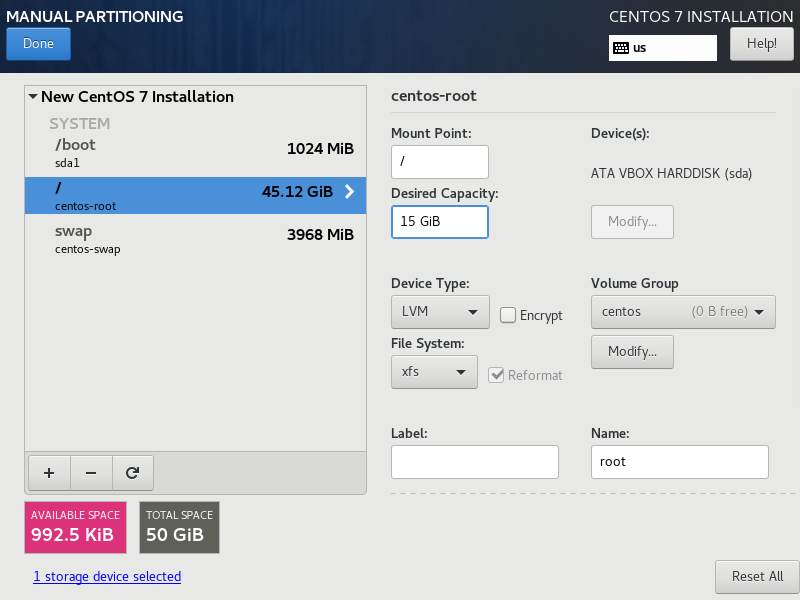
Remove any partition not listed under SYSTEM (if present) and click the + button to add a new one.
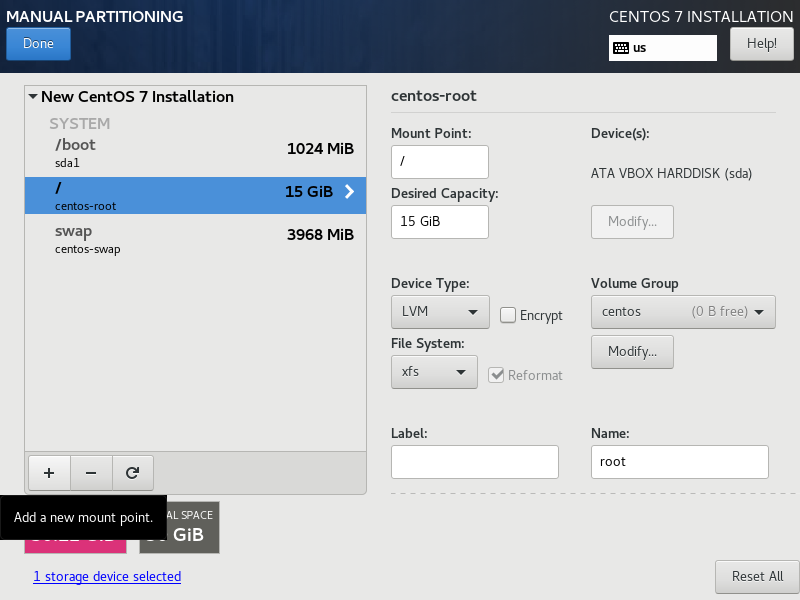
Type /var/lib/docker leave Capacity empty and click on Add mount point.

Check you partition Layout and click on Done.
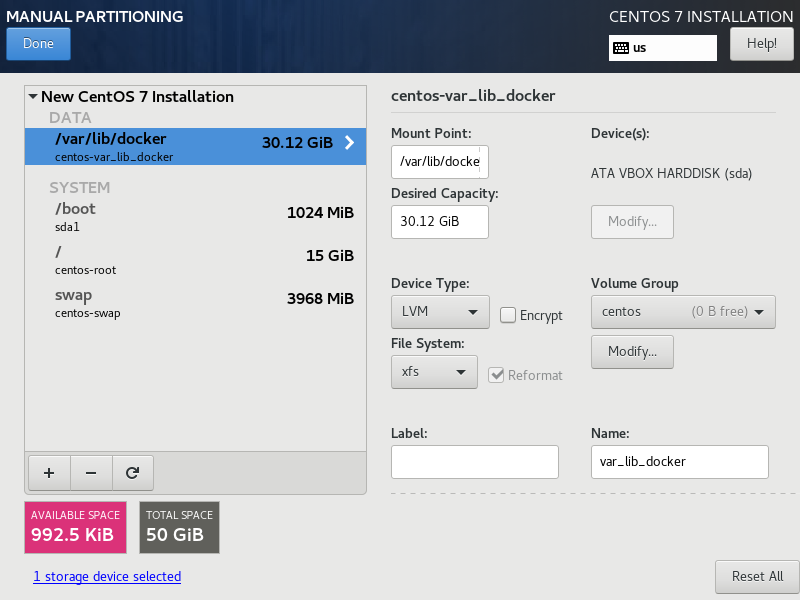
Verify actions and Accept Changes.

Setup networking
Enable the network interface. Set a proper hostname and click Apply. Then click on Configure....
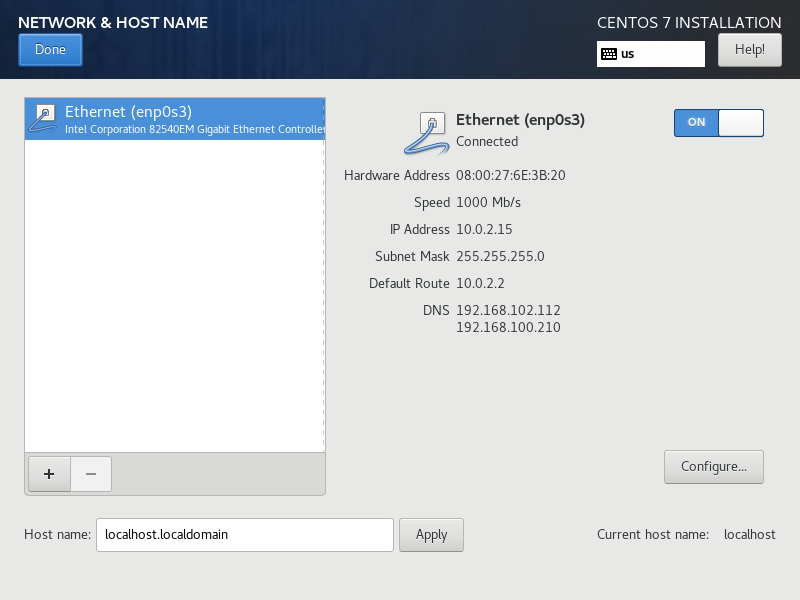
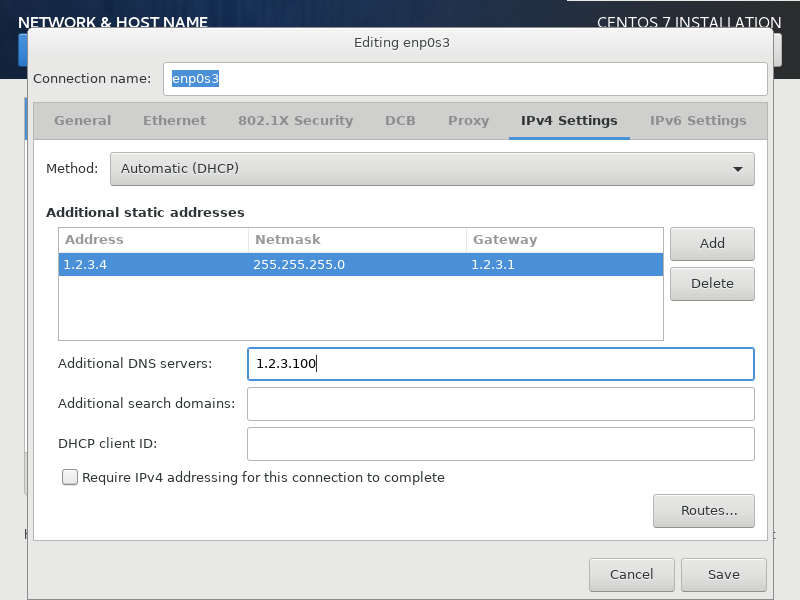
Select the IPv4 Settings tab and set up a static IP. Click on Save then Done.
Click Begin Installation.
While the installation is doing its thing, setup the password for the root-User.
Add a user called admin.
Make sure this user is an administrator.
Reboot the system.
# Post Install
After installing the base system we need to configure the VM to be able to run Docker Containers. We will do a bunch of reboots
# SSH
Log in to your VM using ssh and become the root user.
# Windows
User something like putty (opens new window) to open a ssh shell with admin@[vm-ip]
sudo su
# Linux / MacOS
ssh admin@[vm-ip]
# enter the admin password
sudo su
Note: You need to repeat this steps after every reboot as you will be disconnected!
# Install updates
yum update
# Some handy commandline tools
Execute the following command to install some basic tooling that should not be missing on any Linux machine.
yum install tux vim rsync
# Open VM Tools
As this is a VM we should install open-vm-tools. It's basically vmware guest additions open source alternative and acts alike,
thus the hypervisor VSphere can interact with the VM properly.
yum install -y open-vm-tools
reboot
# Newer Kernel
As we want to run docker it might be a good idea to update to a more recent kernel than the ancient 3.x.x kernel shipped with CentOS7. We need to add the the ELRepo (opens new window) in order to obtain additional kernels. ELRepo provides different kernel streams.
kernel-mlwhich is the main line kernel meaning the latest version Linus Torvalds (opens new window) releases regularlykernel-ltwhich is the long term support version of the kernel
We choose kernel-lt as it's up2date enough and should be "more stable".
rpm --import https://www.elrepo.org/RPM-GPG-KEY-elrepo.org
rpm -Uvh http://www.elrepo.org/elrepo-release-7.0-2.el7.elrepo.noarch.rpm
yum --enablerepo=elrepo-kernel install kernel-lt
After installing the kernel we need to reconfigure the bootloader grub to boot to the latest kernel represented by 0
otherwise it will reboot to the last booted kernel by default.
grub2-set-default 0
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
Check the current kernel version and reboot
uname -r
reboot
Check kernel version again after reboot. It should start with 5 now.
uname -r
# Defuse the SELinux Bomb
CentOS 7 comes with SELinux set to enforce per default, meaning it will most likely block every file interaction per default as well.
We want to change it to permissive to be able to use docker without major headaches.
vi /etc/selinux/config
Change SELINUX=enforce to SELINUX=permissive and save the file.
reboot
Note: You can check the current status of SELinux by running either
getenforceorsestatus.
# Docker-CE
In order to install Docker-CE we need to add their repositories to our CentOS installation
yum install -y yum-utils
yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
Once done we are able to install docker
yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
To enable docker after the next reboot and start it right away execute:
systemctl enable docker
systemctl start docker
We can test the docker installation now using the hello-world image as shown below.
docker run -it --rm hello-world
